In order to meet the requirements of information techniques in the big data era, hardware with strong numeration ability, high integration, and low power consumption is urgently needed. Inspired by the brain, 2D memristors are promising in big data applications such as deep learning, image recognition, and data processing. Currently, memristors have achieved multi-state operation by controlling the migration of ions, but they still suffer from low linearity of conductance variation, poor uniformity, and large operation current.
CuInP2S6 (CIPS) is a kind of layered material that contains intrinsic moveable Cu ions. Ion migration under the electric field can change the resistance of CIPS. Due to the good compatibility of Cu ion and CIPS, it is expected to achieve high-performance memristors based on CIPS.
Recently, Hui-Ming CHENG and Bilu LIU’s research group from Tsinghua Shenzhen International Graduate School (Tsinghua SIGS) has reported a high-performance memristor based on ionic 2D CuInP2S6, in which up to 1350 linear conductance states are achieved by controlling the migration of internal Cu ions in CIPS. In addition, the device shows a low operation current of 100 pA and uniformity. In-situ Scanning Electron Microscope/Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy characterization indicates that the resistance change of CIPS device is related to Cu ion migration under the electric field. In addition, a 2D CIPS-based memristor array can simulate complex signal transport among multiple neurons. These results show that CIPS memristors are potential candidates for future AI devices and open the way for the materials exploration of high-performance memristors.

Figure 1. Structural characterization and Cu ion migration in ionic 2D CIPS

Figure 2. Migration of Cu ions in an ionic 2D CIPS device
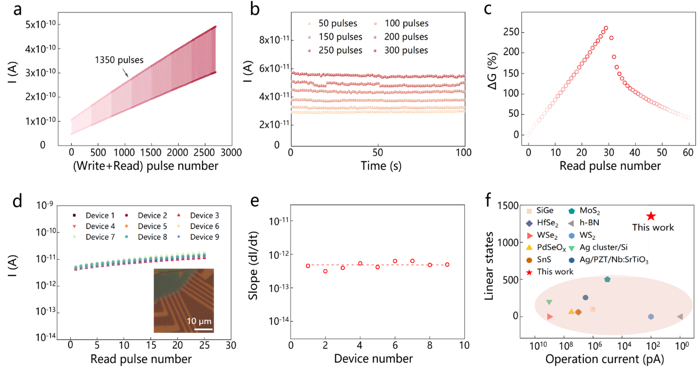
Figure 3. Computation performance of ionic 2D CIPS memristors

Figure 4. Application of CIPS device arrays for complex signal transport
The research paper “Internal ion transport in ionic 2D CuInP2S6 enabling multi-state neuromorphic computing with low operation current” was published in Materials Today recently and it has been chosen for the front cover and as a highlighted paper. The paper’s corresponding authors are Hui-Ming CHENG and Bilu LIU, and the co-first authors are Yujie SUN and Rongjie ZHANG. The authors also include Changjiu TENG, Junyang TAN, Zehao ZHANG, Shengnan LI, Jingwei WANG, Shilong ZHAO, and Wenjun CHEN. This research has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars, Guangdong Innovative and Entrepreneurial Research Team Program, Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, and the Shenzhen Basic Research Program.
Link to the full article:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2023.04.013
Written/Images by Tu Ran
Edited by Alena Shish & Yuan Yang


